Introducing Semantic Reader
An AI-Powered Augmented Scientific Reading Application
What is Semantic Reader?
Semantic Reader is an augmented reader with the potential to revolutionize scientific reading by making it more accessible and richly contextual.
Studies have uncovered many points of friction that break the flow of comprehension when reading technical papers:
- Frequently paging back and forth looking for the details of cited papers
- Challenges recognizing the same work across multiple papers
- Losing track of reading history and notes
- Contending with a PDF format that is not well suited to mobile reading or assistive technologies such as screen readers
To create a better reading experience, Semantic Reader uses artificial intelligence to understand a document’s structure and merge it with the Semantic Scholar’s academic corpus, providing detailed information in context via tooltips and other overlays. If you’re logged-in, Semantic Reader integrates with your library and, over time, will incorporate personalized contextual augmentations as well.

A Revolutionary Reading Experience
Semantic Reader is now available for most arXiv papers on Semantic Scholar with a growing set of features.
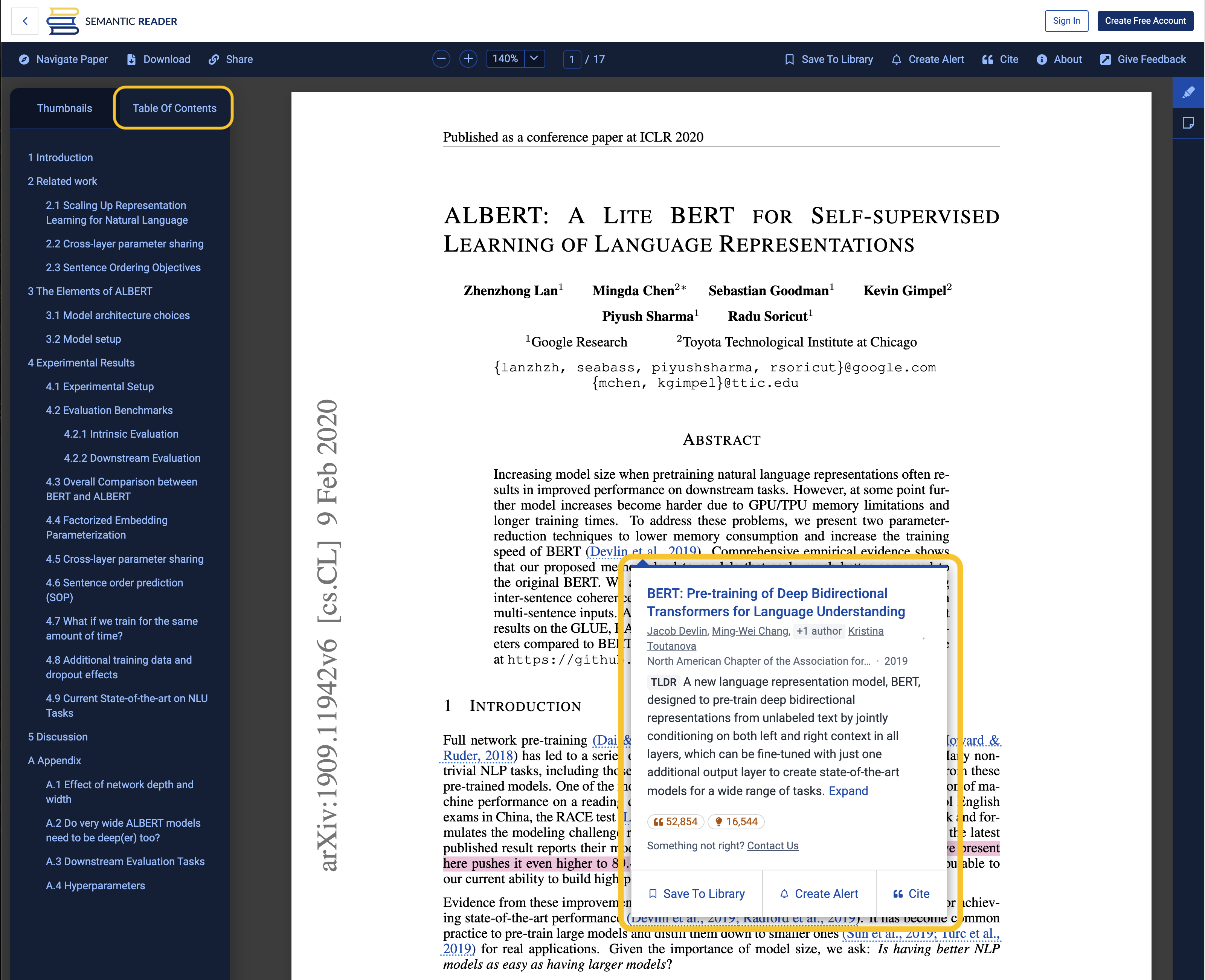
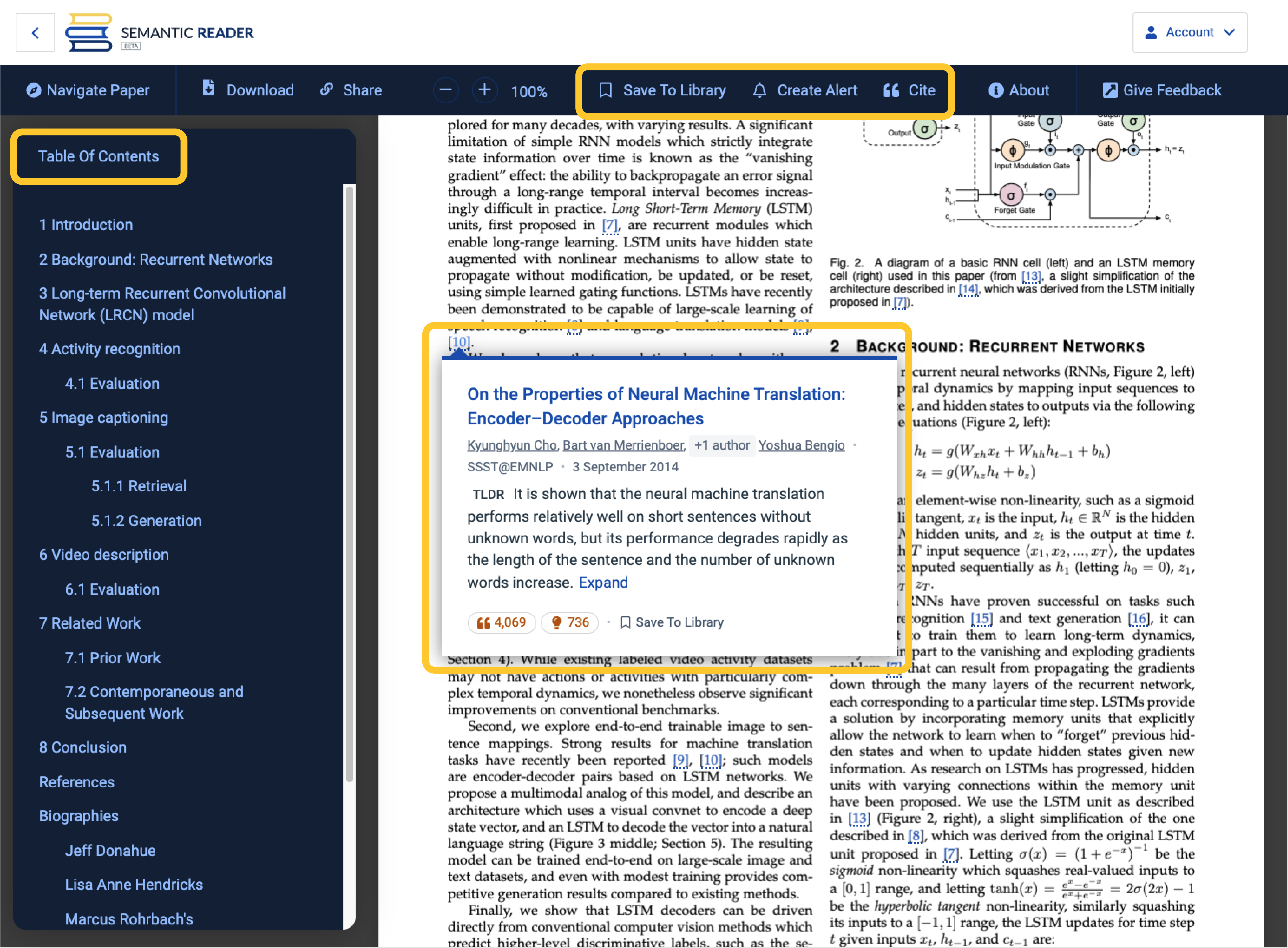
- Citations Cards that show details of a cited paper in-line where you’re reading, including TLDR summaries
- Table of Contents to quickly navigate between sections (availability varies)
- Save to Library to conveniently track your reading list
We are incrementally improving, testing, and rolling out new features in Semantic Reader and expanding coverage to more paper sources.
Subscribe to our Product Spotlight emails for updates!
NEW
Personalized In-line Citations
With the volume and variety of citations during literature review, it can be challenging to prioritize which ones to explore. In Semantic Reader, citations within a paper are visually augmented based on their connections to your research activities, such as saved in your library or cited by a paper in your library.
If you have at least one paper in your library, this feature is available on desktop devices for you! For more details, visit our FAQ.
We plan to introduce visual augmentation for additional types of connections in the coming months. Stay tuned!


BETA
Skim Papers Faster
Find key points of this paper using automatically highlighted overlays. Available in beta on limited papers for desktop devices only.
Try It
Skimming Examples
- BERT: Pre-training of Deep Bidirectional Transformers for Language Understanding
- ALBERT: A Lite BERT For Self-supervised Learning of Language Representations
- Google’s Multilingual Neural Machine Translation System:Enabling Zero-Shot Translation
Annotate and Highlight
With Hypothesis integration, Semantic Reader allows you to highlight and take notes while reading papers.
To access the Annotations panel, highlight some text in Semantic Reader and select Annotate or Highlight. From the panel, sign up for a Hypothesis account and log in. From there, you can post annotations, review your annotations anytime, and share them with others.
For more instructions on using Hypothesis in Semantic Reader, visit our FAQ or Hypothesis help articles.

Try Out Semantic Reader
Here are examples of Semantic Reader operating over popular Computer Science papers across various subfields. The current design is best experienced on a full-size screen.
NLP
Natural Language Processing
- Deep Speech 2: End-to-End Speech Recognition in English and Mandarin
- ALBERT: A Lite BERT for Self-supervised Learning of Language Representations
- Google’s Multilingual Neural Machine Translation System: Enabling Zero-Shot Translation
Send us your Semantic Reader feedback.
Powered by State-of-the-Art Research
Semantic Reader is based on research from the Semantic Scholar team at AI2, UC Berkeley and the University of Washington, and supported in part by the Alfred P. Sloan Foundation.
TLDRThis work introduces ScholarPhi, an augmented reading interface with four novel features: tooltips that surface position-sensitive definitions from elsewhere in a paper, a filter over the paper that “declutters” it to reveal how the term or symbol is used across the paper, automatic equation diagrams that expose multiple definitions in parallel, and an automatically generated glossary of important terms and symbols.
TLDRA novel paper reading experience that integrates relevant information about follow-on work directly into a paper, allowing readers to learn about newer papers and see how a paper is discussed by its citing papers in the context of the reference paper.
TLDRScim is presented, an AI-augmented reading interface designed to help researchers skim papers by automatically identifying, classifying, and highlighting salient sentences, organized into rhetorical facets rooted in common information needs.